Introduction to Zero-Touch Networks
5G/6G Zero-Touch Networks represent a revolutionary paradigm shift in networking, enabling self-optimizing, autonomous, and self-configuring networks. Edge computing plays a critical role in Zero-Touch Network and Service Management (ZSM), providing efficient resource allocation and dynamic service provisioning across the cloud-edge continuum. ETSI ISG ZSM outlines general requirements for this reference framework, including energy efficiency, QoS, availability, compliance, interoperability, standardization, and security. OpenNebula significantly contributes to meeting these requirements through capabilities in Domain Control, Domain Data Collection, and Domain Orchestration.
AI-driven resource management for 5G/6G edge infrastructures and ZSM environments leverages multiple ML techniques, such as multi-tenancy management, traffic monitoring, and architecture coordination, among others. For optimal placement of 5G CNF and VNF in hybrid deployments, various performance metrics, methods, algorithms, and environments are employed, analyzing placement approaches based on heuristics and ML algorithms.
OpenNebula’s Accomplishments
A 5G architecture based on the cloud-edge continuum is a highly distributed system that spans multiple network locations, enabling the deployment of high-throughput, low-latency applications. OpenNebula orchestrates and maintains this system lifecycle—from physical infrastructure to application—fulfilling the following high-level characteristics:
- Application components are distributed across multiple edge locations to reduce latency and traffic between components.
- Delivers applications as-a-service, with the entire stack (including Network Functions (NF) and infrastructure) automatically provisioned in the most suitable location and its life-cycle managed by a common orchestration layer.
- A distributed application that requires the deployment of multiple components across multiple cloud-edge locations to optimize performance and minimize latency.
In activities run with i2cat, OpenNebula is the primary orchestration component for such a framework offering advanced orchestration functionalities for virtualized infrastructures. It is responsible for deploying and managing distributed applications across selected edge locations, along with associated elements like virtual networks, using its internal Software-Defined Networking (SDN) capabilities. OpenNebula also provides a multitenancy and isolation layer to ensure that distributed applications can coexist seamlessly within the system.
A high degree of automation is needed to efficiently deploy and operate such a complex system. OpenNebula includes a module to automatically provision and configure edge locations, using hyper-convergent solutions, enabling the use of a broader type of edge locations. As B5G application workloads are quite dynamic and can experience significant increases during specific situations or periods, a predefined schedule and behavior for scaling workloads can lead to overprovisioning (underutilization of compute resources) or under-provisioning (degradation of application performances and service quality). To address this, OpenNebula includes a programmatic way to define the architecture and technologies that enable infrastructure connectivity to benefit from heterogeneous domains spread across the cloud-edge continuum. It also offers a declarative definition to express various configurations of edge clusters, facilitating the validation of different provider profiles and locations.
OpenNebula was extended with new AI-powered features that bring enhanced operational insight and predictive capabilities. These extensions include integration with advanced telemetry (in collaboration with OPTARE Solutions), and in addition AI features were strengthened with automated AI pipelines for ML model training, validation, and deployment. The integration of these components is key to achieving the vision of zero-touch network and service management, which is defined by the automated and predictive orchestration of network resources.
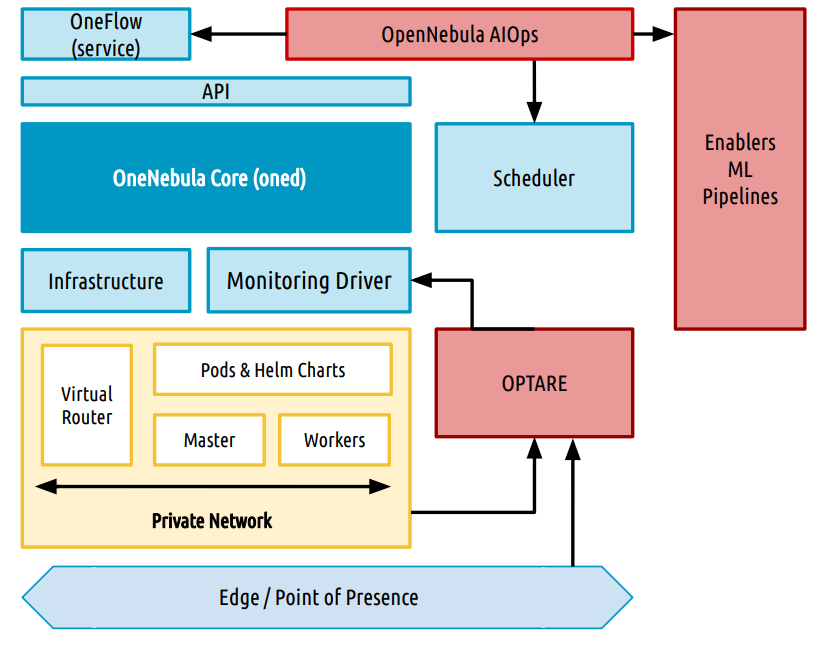
Traditional scaling approaches, which rely on elasticity rules based on monitored metrics like CPU or memory usage, react only after changes are needed, resulting in service and performance degradation for applications. OpenNebula’s approach is different. Leveraging advanced machine learning algorithms trained on a vast amount of historical data related to a wide range of metrics, including resource usage, network traffic, application performance, external factors like time of day, and user-defined metrics, the AIOps module can predict future workload demands more accurately and make more informed decisions, enabling more proactive and efficient scheduling and scaling strategies.
This new framework has significantly extended OpenNebula’s capabilities by incorporating new features and components designed to improve network resource management. These improvements include the integration of a new monitoring system, enhanced orchestration and management for Kubernetes clusters, and the integration of advanced machine learning (ML) models for predictive analytics and proactive management. These enhancements are crucial for enabling zero-touch orchestration, which is essential for efficiently managing the complexities of 6G networks.
Conclusion
In this context, the efficient and intelligent orchestration of geographically distributed edge-cloud infrastructures is crucial for automating the management, placement, and scaling of NFs in 5G/6G networks. This plays a key role in advancing zero-touch network and service development. The transition to 6G networks requires a paradigm shift in network management strategies to meet the growing complexity, speed and connectivity demands.
We have integrated cloud-edge continuum and AI technologies to facilitate intelligent, zero-touch network and service management—essential for the 6G era. These initiatives leverage the OpenNebula Cloud Platform as the core infrastructure, selected for its flexibility, robustness, and its capabilities in managing and orchestrating Network Functions across the cloud-edge continuum.

This initiative is funded by the Spanish Ministry for Digital Transformation and Civil Service through the project titled “Zero-Contact Technologies for Adaptation in Intelligent and Distributed 5G Networks – 6GENABLERS: AI for 6G, Ultra Automation and Optimization (TSI-063000-2021-10)” and co-financed by the European Union’s NextGenerationEU program via the Recovery and Resilience Facility (RRF).




0 Comments