In today’s complex IT landscape, managing cloud infrastructure efficiently is more critical than ever. As environments scale, so do the challenges of day-to-day operations. Teams often find themselves navigating complex GUIs or memorizing an ever-growing list of CLI commands to perform even routine tasks. What if you could manage your cloud as easily as having a conversation?
Today, we’re excited to introduce a revolutionary step forward in cloud management: the OpenNebula MCP Server. This new, AI-powered co-pilot for your OpenNebula environment is designed to understand your intent and translate simple, natural language commands into complex cloud operations, making infrastructure management more intuitive, accessible, and powerful.
The Foundation: What Is the Model Context Protocol (MCP)?
Before diving into the OpenNebula MCP Server, it’s important to understand the technology that powers it: the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
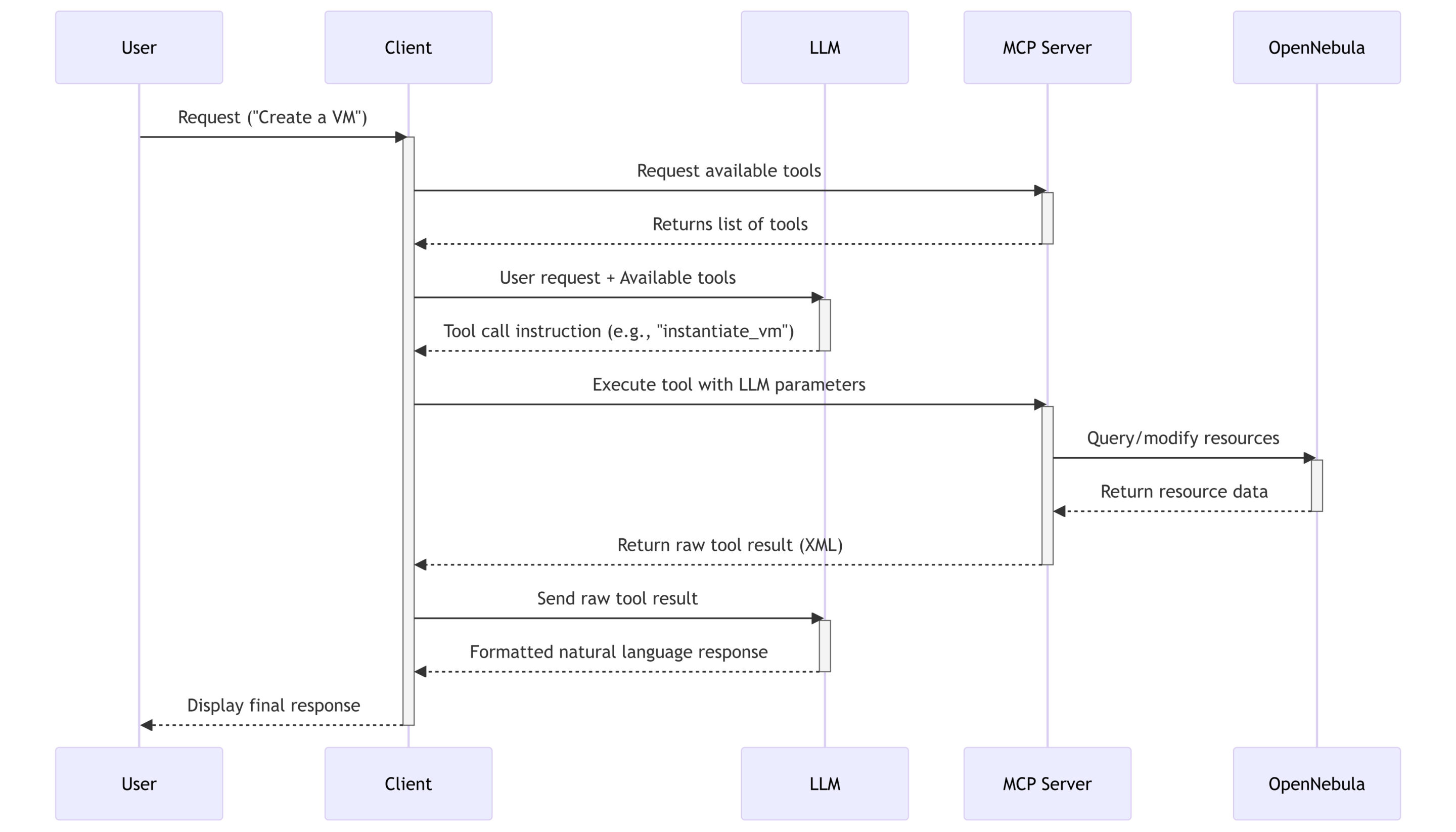
MCP is a groundbreaking open protocol designed to standardize communication between Large Language Models (LLMs) and external tools or APIs. Think of it as a universal protocol that allows an AI to discover, understand, and use a given set of tools in a structured and reliable way.
Instead of just processing text, an MCP-enabled LLM can interact with its environment, query systems, and execute commands. This is crucial because it moves beyond simple chat and into the realm of autonomous, tool-augmented intelligence. It ensures that when you ask an AI to perform a task, it has a robust and more predictable way to interact with the systems required to get the job done.
Choose Your Client: A Key Advantage of the MCP Standard
One of the most powerful advantages of building on the open Model Context Protocol is the freedom it gives you to choose your client. Because the OpenNebula MCP Server speaks a standard language, you’re not locked into a single interface. You can interact with your OpenNebula cloud using any MCP-compliant client that fits your workflow.
This means you can manage your cloud from the environment where you are most productive. Whether you are a CLI power user, a DevOps engineer building automation pipelines, or a developer who lives in their IDE, there’s a client for you. For example:
- For the Terminal and Automation: Use a CLI client like mcphost or VSCode with the CLINE plugin to manage infrastructure directly from the command line, create powerful shell scripts, or integrate cloud operations into your CI/CD pipelines.
- For Integrated Workflows: Connect to the server from modern, AI-enabled terminals like Warp or directly within your editor using tools like Cursor—bringing powerful cloud management capabilities right into your development environment.
This flexibility is central to our vision: bringing cloud control to you, in the tools you already use and love.
The OpenNebula MCP Server: Your Cloud’s Native AI Interface
The OpenNebula MCP Server is our implementation of this powerful protocol, built specifically for the OpenNebula ecosystem. It acts as a smart, conversational interface—a centralized brain for your cloud. Instead of telling your infrastructure how to do something with a rigid set of commands, you simply tell the MCP what you want to achieve.
Want to deploy a three-node web server cluster? Just ask. Need to check on the health of your production hosts and find any offline VMs? Just ask. The MCP server parses your request, understands the context, executes the necessary sequence of actions, and delivers the result.
See It in Action: Watch Our Screencast
Reading about it is one thing, but seeing it live is another. Watch our new screencast to see just how easy it is to manage your OpenNebula cloud with the MCP Server.

From Complex Scripts to Simple Conversations: Use Cases
The true value of the OpenNebula MCP comes to life when you see it in action. Let’s explore a few common scenarios where the MCP turns complex operational hurdles into simple conversational tasks.
1. Infrastructure and VM Health Checks
- The Old Way: You’d run `onehost list` or `onevm list` or `onevnet list`, then manually cross-reference the output to correlate the hosts, VMs, and virtual networks currently available.
- The MCP Way: A single prompt: “Show me the status of my hosts in the production cluster and list any VMs that are not running.”
2. Stateful Application Deployment
- The Old Way: This required a script. You’d instantiate a VM, poll its status until it was running, retrieve its new IP address, and then SSH in to install and start Nginx. A non-trivial, multi-step process.
- The MCP Way: A single prompt: “Can you create a VM based on Ubuntu 22 with a NIC on the service network, with 1 CPU and 2GB? Call it “MCPWebServer”.
3. Instant, AI-Powered Troubleshooting
- The Old Way: An application is down. You find the VM’s IP, SSH into the machine, run `systemctl status nginx`, check the logs with `journalctl`, and `tail` the error logs. This involves significant context-switching and deep technical knowledge.
- The MCP Way: A single prompt: “My application on ‘web-server-prod’ is down. Check the status of the nginx service and show me the last 10 lines from its error log.”
The Future of Cloud Management Is Conversational
The OpenNebula MCP Server represents more than just a new tool—it’s a new philosophy for cloud management. By leveraging a standardized protocol like MCP, we’re building a future where interacting with complex infrastructure is as simple and intuitive as talking to a colleague. By lowering the barrier to entry for complex operations, it democratizes cloud administration, boosts productivity, and reduces the potential for human error.
Ready to start a new conversation with your cloud?
- Explore the Project on GitHub
- Watch the Screencast Demo
- Join the discussion on our Community Forum.
Register here for our live webinar to dive deeper into this topic, get a full walkthrough, and ask your questions directly to the experts.





0 Comments